Download Assets
description
Learn to use Clipping Masks in Photoshop! This tutorial shows how to apply images to text and shapes, or even constrain effects to a cut-out subject. Discover the benefits over layer masks, easy methods, and ways to customize your design with shadows and blending.
Go PRO:
Dive deeper into the world of Photoshop with our in-depth PRO Photoshop Learning Path . Across 11 courses and 53 hours of engaging content, you’ll learn Photoshop’s ins and outs, master pro-level tools, and tackle fun and challenging projects..
Image Source
- Anusmit Sil
- Betul Gunes
Image sourced from Pexels.
Share
AFTER
BEFORE
Clip & Create
Clipping masks are a powerful, non-destructive feature in Photoshop that allows you to control the visibility of one layer’s content based on the shape of another layer directly beneath it. Understanding how to use them enables precise control over textures, adjustments, and effects without permanently altering your source images, maintaining a highly flexible and editable workflow.
Prepare Your Assets
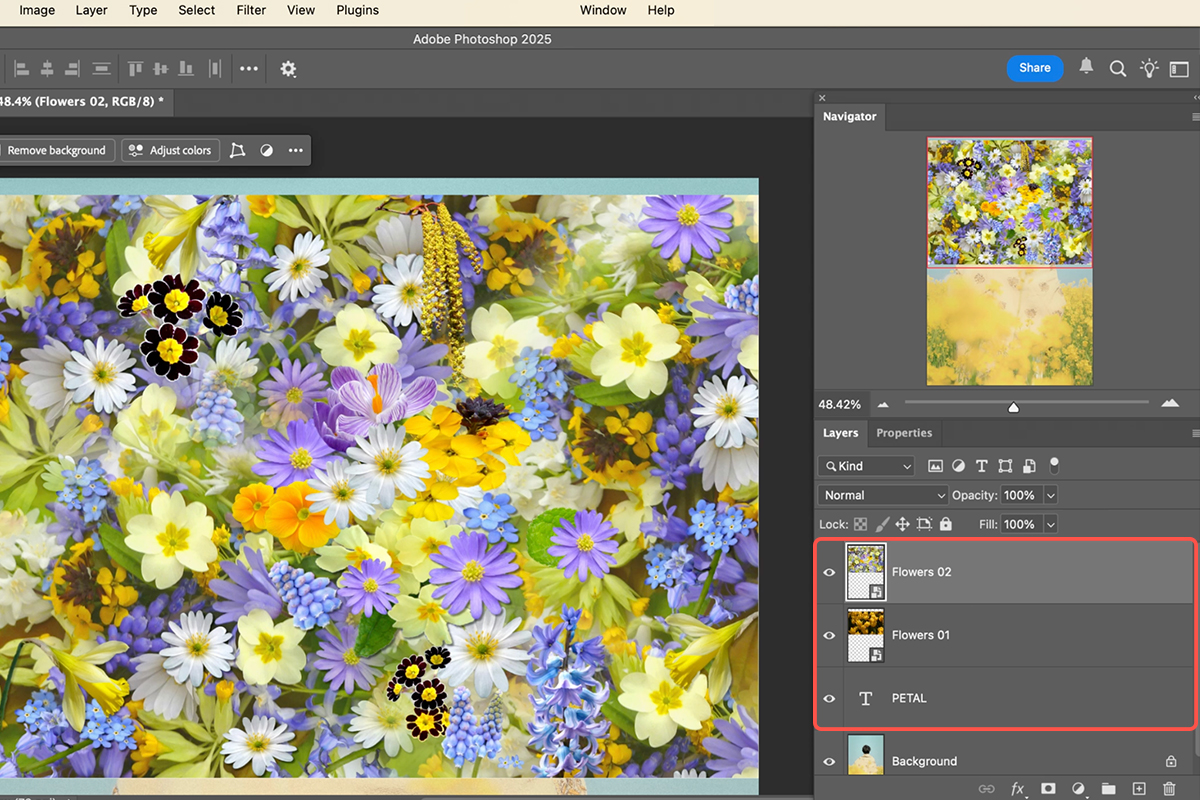
Start by arranging your layers in the desired order.
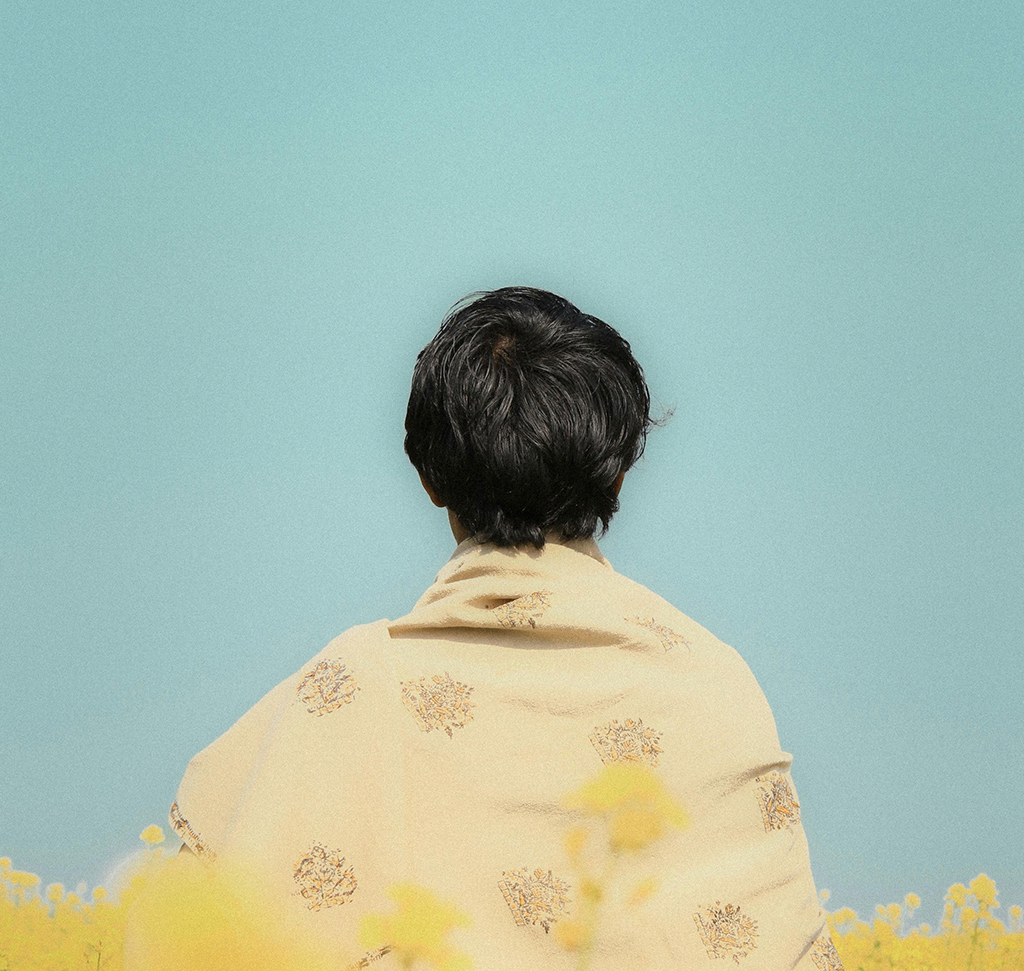
1. First, have your main background image with the subject.
2. Next, create a layer for the object you want to clip to, such as large, thick text (the tutorial uses “petal”) or a simple vector shape (a rounded rectangle is shown).
3. Finally, drag the image(s) you want to use as the texture onto the canvas, making sure these texture layers are positioned directly above the base text or shape layer in the Layers panel. The base layer defines the visible boundaries for all layers clipped to it.
Using Clipping Masks
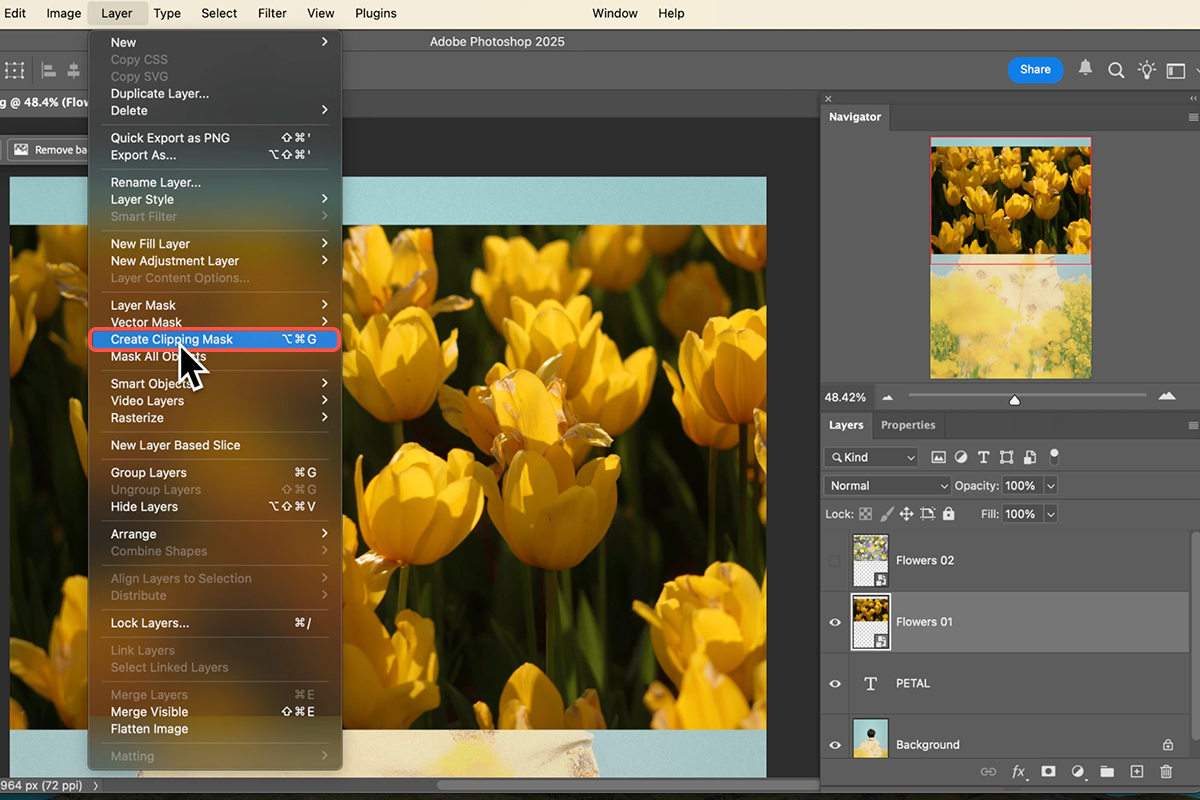
4. With your texture layer directly above the desired base layer (text or shape), you are ready to create the clipping mask. There are two primary ways to do this:
Mouse Method: Hold down Alt/Option, and hover your cursor directly over the dividing line between the top texture layer and the base layer in the Layers panel. Your cursor will turn into a square with a down arrow . Click once to apply the mask.
Keyboard Shortcut: Select the texture layer and press Ctrl + Alt + G (Windows) or Command + Option + G (Mac). Once clipped, the texture layer will be indented and show a down arrow, indicating it is now visible only within the pixels of the layer beneath it. You can clip multiple layers to a single base layer.
Edit & Adjust
The key benefit of clipping masks is flexibility. You can independently adjust both the base layer and the clipped texture layers:
Moving: Use the Move Tool (V) to reposition the clipped image (e.g., move the flowers within the text boundary) or reposition the entire base text layer, and the clipped content will follow.
Content Change: Double-click the base text layer to change the words (for example from “petal” to “flower”). The clipping mask remains functional without any further steps.
Blending/Color: Select the clipped image layer to apply image adjustments like Levels (Ctrl/Cmd + L) or Hue/Saturation (Ctrl/Cmd + U), or add a layer style like a Drop Shadow to the base text layer to enhance the effect.
Subject Placement
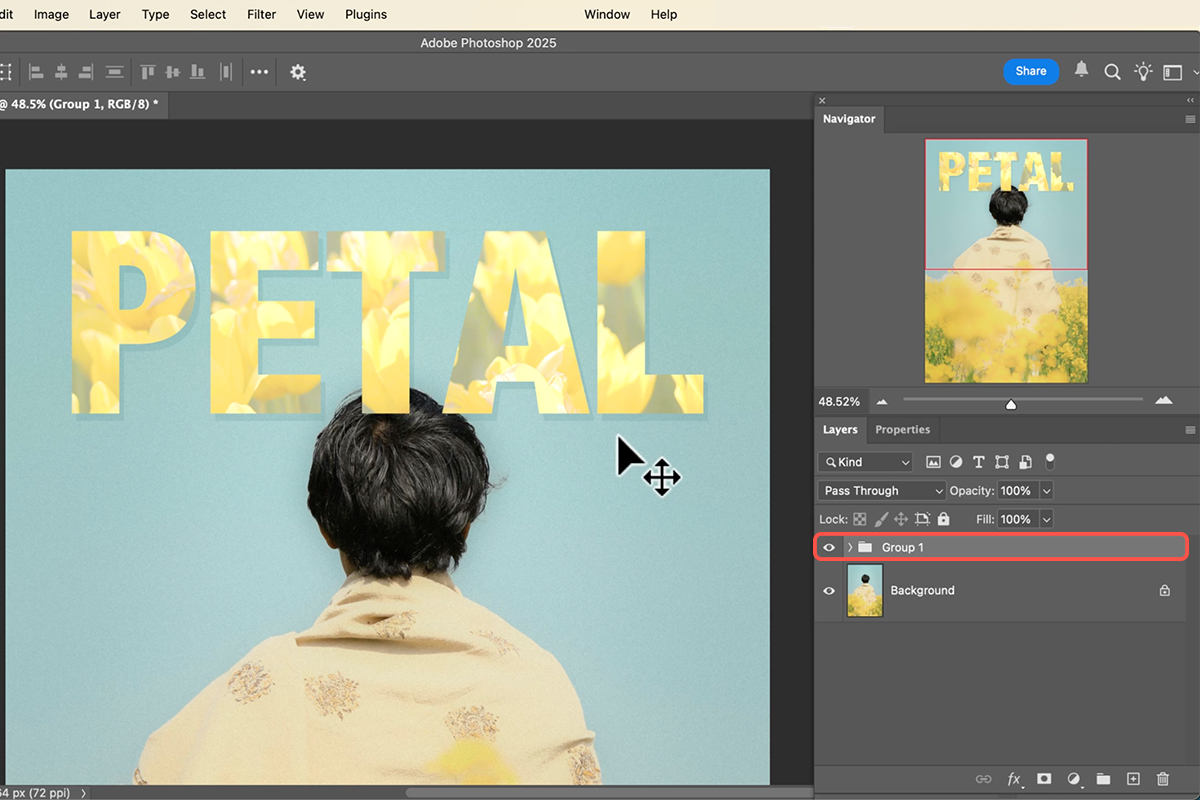
For a complex composite effect, you can place the final text/texture design behind a subject in the background image:
1. Group your clipping mask setup (all texture layers and the base text layer) by selecting them all and pressing Ctrl/Cmd + G.
2. Go back to your background layer, and use Select Subject from the Contextual Task Bar.
3. With the subject selection active, select the newly created Group in the Layers panel.
4. Hold Alt/Option and click the Add Layer Mask icon at the bottom of the Layers panel. This creates a mask on the group that hides the text wherever the subject is, effectively placing the text behind them.